In today’s hyper-connected world, weak cell phone signals can be a major frustration, whether you’re trying to make an important call or access data on the go. Poor reception can happen for various reasons, including distance from a cell tower, obstructions like thick walls, or natural barriers such as hills. Fortunately, cell phone signal boosters exist to resolve these connectivity issues, ensuring that weak signals are amplified and you stay connected no matter where you are.
This article will dive deep into how cell phone signal boosters work, the technology behind them, and why they’re such an effective solution for improving cell phone reception.
What is a Cell Phone Signal Booster?
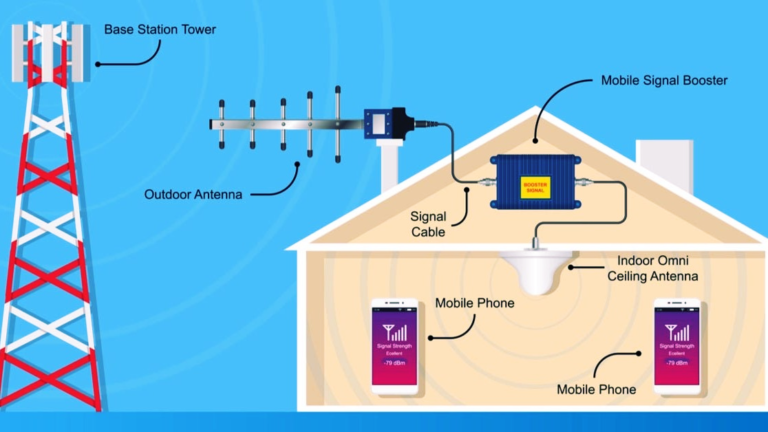
A cell phone signal booster (also known as a repeater or amplifier) is a device that takes a weak cellular signal from the outside, amplifies it, and then rebroadcasts it inside your home, office, or vehicle. Essentially, it strengthens the available cell signal so that your mobile devices can connect more reliably for calls, text messages, and data usage.
Signal boosters consist of three main components:
- An External Antenna: This captures the weak signal from the cell tower.
- An Amplifier: This boosts the strength of the captured signal.
- An Internal Antenna: This rebroadcasts the amplified signal inside the area where you need better coverage.
The goal of a signal booster is simple: it amplifies an existing weak signal to improve cell phone reception, ensuring clearer voice calls, faster data speeds, and fewer dropped connections.
How Does a Cell Phone Signal Booster Work?
The way cell phone signal boosters work is both simple and efficient. Let’s break it down step-by-step:
Step 1: Capture the Existing Cellular Signal
The first step in the process is capturing the existing signal outside your home, office, or vehicle. This is done using an external antenna, which is usually installed on the roof or in a location where the signal is the strongest. The antenna’s job is to pull in whatever signal is available from the nearest cell tower, even if it’s faint or unstable.
There are two main types of external antennas:
- Omnidirectional Antenna: This antenna captures signals from all directions, making it ideal for areas where cell towers are distributed in different locations.
- Directional Antenna (Yagi Antenna): This antenna focuses on capturing the signal from a single direction, which is useful when you know where the closest cell tower is located. Directional antennas can often capture weaker signals over greater distances compared to omnidirectional ones.
Step 2: Amplify the Signal
Once the external antenna captures the weak signal, it sends it to the amplifier, the core component of the signal booster system. The amplifier’s job is to boost the strength of the captured signal. Amplifiers are measured in decibels (dB), which indicates the level of signal improvement they provide. The higher the dB gain, the stronger the signal amplification.
The signal boost is critical because it ensures that even a weak signal from far away can be made strong enough to be usable indoors. For areas with extremely weak signals, a more powerful amplifier is required to boost the signal effectively.
Step 3: Rebroadcast the Amplified Signal
Once the signal is amplified, it is sent to the internal antenna, which is installed inside the building or vehicle. The internal antenna’s role is to rebroadcast the strengthened signal throughout the desired area. This allows mobile devices such as cell phones, tablets, and even hotspots to connect to a stronger signal, improving call quality, data speeds, and overall network reliability.
Like the external antenna, there are different types of internal antennas:
- Panel Antenna: This antenna broadcasts the signal in a specific direction, making it ideal for hallways or rooms with long layouts.
- Dome Antenna: This type of antenna broadcasts the signal in all directions, making it more suitable for open areas or large rooms.
By strategically placing the internal antenna, you can ensure that the boosted signal covers all areas of your home or office, providing seamless connectivity.
The Components of a Signal Booster System
Understanding the components of a signal booster system helps explain how each part plays a role in amplifying and rebroadcasting the signal. Here’s a closer look at the key elements:
1. External Antenna
The external antenna is placed outside the building or vehicle to capture the weak signal from nearby cell towers. This antenna is crucial because it ensures that the booster has a signal to work with. Its effectiveness depends on its type (omnidirectional or directional) and its placement.
For optimal performance, the antenna should be installed in the location with the strongest signal, such as the rooftop or a high wall, and in the direction of the closest cell tower.
2. Amplifier
The amplifier is the heart of the signal booster system. It increases the power of the weak signal that the external antenna captures. Signal amplifiers are rated based on their gain, measured in decibels (dB). The higher the gain, the more powerful the signal becomes, and the larger the coverage area it can support.
Different amplifiers are available for different needs. Some are designed for homes or small offices, while others are built for larger spaces, vehicles, or areas with exceptionally weak signals.
3. Internal Antenna
The internal antenna is placed inside the building or vehicle to rebroadcast the amplified signal. This ensures that all mobile devices within the coverage area benefit from the improved signal. The type of internal antenna you choose depends on the layout of your space and the coverage area needed.
For large spaces or multi-level homes, multiple internal antennas might be required to ensure even coverage across all rooms and floors.
Factors That Affect Signal Booster Performance
While signal boosters are highly effective in improving cell reception, their performance can be influenced by various factors:
- Distance from the Cell Tower: The further you are from the nearest cell tower, the weaker the signal will be. A powerful booster with a high-gain external antenna may be needed to capture a usable signal in such cases.
- Obstructions: Physical barriers such as thick walls, trees, or mountains can block signals from reaching your phone. Signal boosters work best when there is a clear line of sight between the external antenna and the cell tower. If there are obstructions, a directional antenna may help by focusing on a specific tower.
- Carrier Frequency Bands: Signal boosters work on specific frequency bands used by cellular providers. It’s essential to ensure that your signal booster is compatible with the frequency bands used by your carrier. Most modern boosters are multi-band and support all major networks.
- Installation: The correct installation of the external and internal antennas can significantly impact the booster’s performance. Placing the external antenna in an optimal location where the signal is strongest and ensuring proper spacing between the external and internal antennas will minimize interference and maximize signal strength.
Benefits of Using a Cell Phone Signal Booster
Cell phone signal boosters provide several key benefits for individuals living or working in areas with weak signals:
- Fewer Dropped Calls: Boosters enhance the signal strength, reducing the likelihood of dropped calls.
- Improved Voice Quality: Clearer voice communication is a major benefit of amplified signals.
- Faster Data Speeds: Boosters improve data transmission, leading to faster internet browsing, downloads, and streaming.
- Extended Coverage: Signal boosters ensure that the entire area within your home, office, or vehicle is covered by a stronger signal.
- Better Battery Life: When your phone has a strong signal, it doesn’t need to work as hard to maintain a connection, leading to longer battery life.
Conclusion: A Simple Solution for Stronger Connectivity
Cell phone signal boosters are an effective, reliable solution for improving weak signals in homes, offices, and vehicles. By capturing, amplifying, and rebroadcasting cellular signals, they provide clearer calls, faster data speeds, and more consistent connections. With the right booster system in place, you can eliminate the frustration of poor reception and stay connected when it matters most.
Understanding how these devices work and choosing the right one for your needs ensures you’ll get the best possible performance, keeping you connected no matter where you are.