Maintaining a strong cell phone signal is particularly difficult in metal buildings, including factories, warehouses, and even some contemporary homes with metal roofs. Cell signals are also blocked or weakened by the very components that give these buildings their durability, such as metal roofing, walls, and support columns. Because of this, people who live or work in metal buildings frequently experience slow data speeds, poor voice quality, and dropped calls. Fortunately, there is a practical way to get around this issue: cell phone signal boosters. What you need to know about installing a signal booster to improve connectivity within a metal structure, why metal structures block cell signals, and how signal boosters operate in metal environments are all covered in this article.
Why Do Metal Buildings Block Cell Signals?
To understand why metal buildings cause weak cell signals, it’s important to know how cell signals travel. Cell signals are radio waves that travel through the air, much like signals for radio, television, or Wi-Fi. However, certain materials are highly effective at blocking or reflecting these signals, preventing them from reaching their intended destination. Metal is one of the most notorious materials for causing signal loss.
Key Factors Contributing to Signal Blockage:
- Metal as a Signal Barrier: Metal is highly reflective, meaning that when radio waves, including cell signals, hit a metal surface, they are either absorbed or reflected away. This significantly weakens the signal before it can enter the building.
- Signal Reflection: Inside metal buildings, signals can bounce around without reaching your device. This creates areas of poor reception or “dead zones” where no signal is available at all.
- Dense Materials: Metal is often combined with other dense building materials like concrete or insulation, which further reduces the strength of any signal trying to penetrate the structure.
- Distance from Cell Towers: If a metal building is located far from the nearest cell tower, the weak signal that does manage to reach the structure may not be strong enough to penetrate the walls, leading to poor reception inside.
The result is that, without intervention, even if your phone shows good signal strength outdoors, you may have little or no reception inside a metal building.
How Do Signal Boosters Work in Metal Buildings?
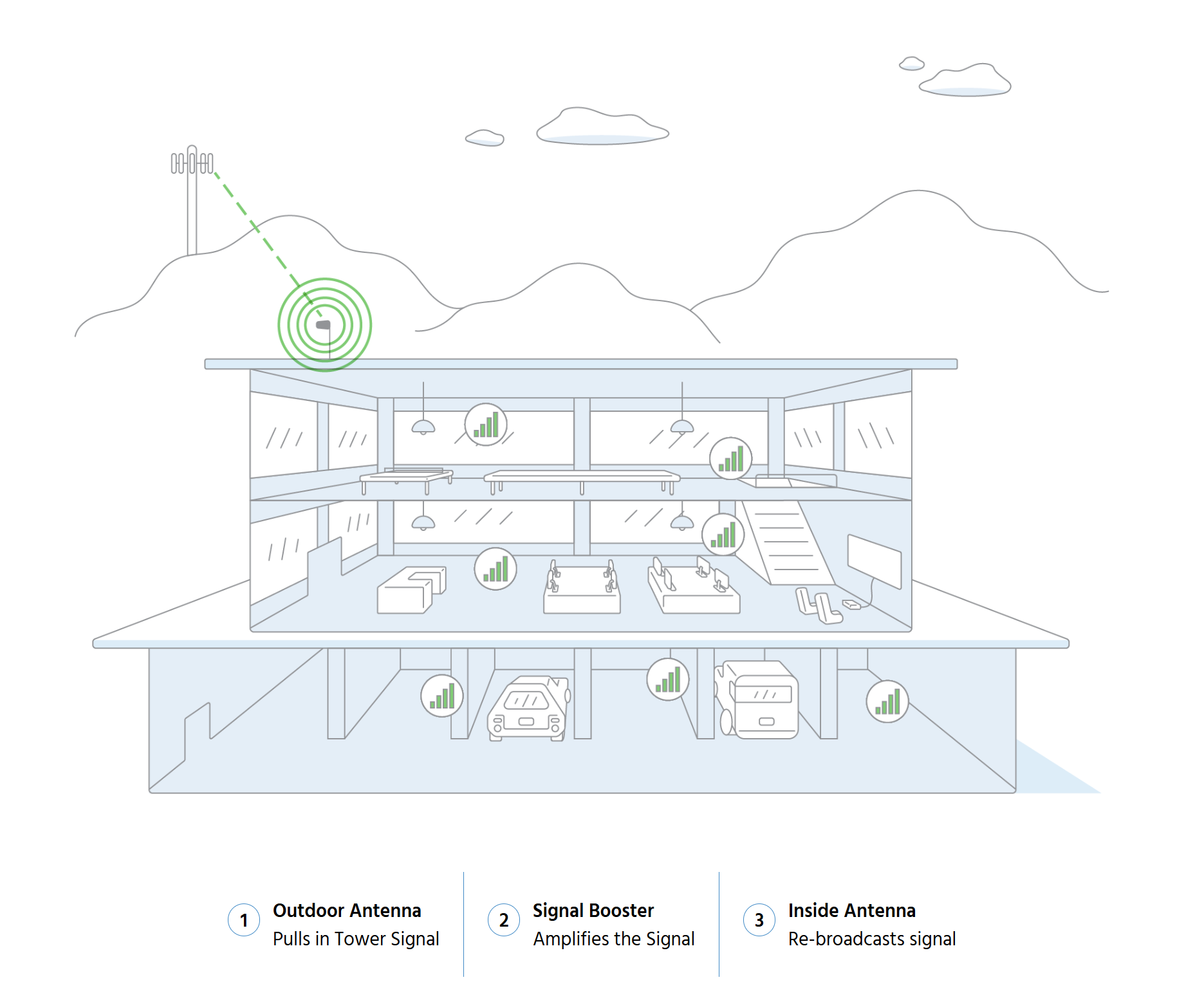
A cell phone signal booster amplifies weak signals from outside the building and rebroadcasts them indoors, helping to overcome the signal loss caused by metal walls and roofs. Signal boosters are particularly effective in metal buildings because they bridge the gap between weak outdoor signals and blocked indoor spaces.
How a Signal Booster Works:
- Capturing the Signal: The signal booster system begins with an outdoor antenna, which is typically mounted on the roof or an exterior wall. This antenna captures whatever signal is available outside the building, even if it’s weak. In the case of metal buildings, the outdoor antenna is critical because it bypasses the barrier created by the metal structure.
- Amplifying the Signal: Once the outdoor antenna captures the signal, it is sent to the amplifier. The amplifier boosts the signal strength, making it powerful enough to be distributed inside the building.
- Rebroadcasting the Signal: After amplification, the signal is sent to the indoor antenna, which rebroadcasts the boosted signal throughout the interior space. This allows all cell phones and mobile devices inside the building to enjoy improved reception, clearer calls, and faster data speeds.
By using a signal booster, metal buildings that previously blocked or degraded cell signals can become areas of reliable connectivity.
Benefits of Using Signal Boosters in Metal Buildings
Installing a signal booster in a metal building offers several benefits:
1. Improved Call Quality
Metal buildings are notorious for causing dropped calls or poor voice quality. With a signal booster, the indoor antenna ensures that you maintain strong, stable connections, reducing the likelihood of dropped calls and improving voice clarity.
2. Faster Data Speeds
For those using mobile data to browse the internet, stream content, or use cloud-based services, signal boosters can significantly improve data speeds. This is especially important in commercial metal buildings where slow data can hinder productivity.
3. Broader Coverage
Signal boosters are designed to cover large areas, which is especially useful in expansive metal buildings such as warehouses or factories. By installing multiple indoor antennas, you can extend coverage to all corners of the building, ensuring that no area is left with poor reception.
4. Supports Multiple Devices
Most signal boosters are designed to support multiple devices and carriers simultaneously. This means that everyone working or living in the building, regardless of their mobile provider, will benefit from enhanced signal strength.
5. Increased Battery Life
When your phone is constantly searching for a signal, it uses more battery power. A stronger, more consistent signal provided by a booster means that your phone doesn’t have to work as hard to maintain a connection, resulting in longer battery life.
Key Considerations for Installing a Signal Booster in a Metal Building
Installing a signal booster in a metal building requires careful planning to ensure the best possible results. Here are some key factors to keep in mind:
1. Outdoor Antenna Placement
Proper placement of the outdoor antenna is critical in a metal building. Since metal walls and roofs block signals, the outdoor antenna must be placed outside the structure, ideally on the roof, where it can capture the strongest possible signal from the nearest cell tower. The higher the placement, the better the chances of capturing a clear, unobstructed signal.
- Clear Line of Sight: The outdoor antenna should have a clear line of sight to the nearest cell tower, free from obstructions such as trees, hills, or other buildings.
- Aiming the Antenna: For best results, especially in rural areas or where the signal is weak, use a directional antenna and aim it toward the nearest cell tower. This ensures that the antenna focuses on capturing the strongest available signal.
2. Indoor Antenna Placement
The placement of the indoor antenna is just as important as the outdoor antenna. Indoor antennas rebroadcast the amplified signal, so they need to be strategically placed to ensure the signal reaches all areas of the building.
- Central Location: To maximize coverage, place the indoor antenna in a central location where the signal can be distributed evenly throughout the space.
- Use Multiple Antennas for Large Buildings: In large metal structures like warehouses or multi-floor buildings, a single indoor antenna may not be sufficient to cover the entire area. In such cases, consider installing multiple indoor antennas to ensure comprehensive coverage.
3. Antenna Separation
One important consideration when installing a signal booster system is ensuring that the outdoor and indoor antennas are far enough apart to avoid interference. In metal buildings, this can be especially important due to the reflective nature of metal surfaces. If the antennas are too close together, the system may create feedback loops, reducing the effectiveness of the booster.
- Vertical or Horizontal Separation: The general recommendation is at least 20 feet of vertical or horizontal separation between the outdoor and indoor antennas, but this can vary depending on the specific booster system.
4. Cable Routing
Signal boosters require coaxial cables to connect the outdoor antenna to the amplifier and the amplifier to the indoor antenna. In metal buildings, it’s important to route these cables carefully to avoid damage or signal degradation.
- Use the Shortest Path Possible: The longer the cable, the more signal loss you’ll experience. Aim to use the shortest, most direct path when running cables between antennas and the amplifier.
- Avoid Sharp Bends: Ensure that the cables are not bent or twisted, as this can degrade the signal and reduce the performance of the booster.
Common Challenges When Boosting Signals in Metal Buildings
While signal boosters can significantly improve cellular reception in metal buildings, there are some challenges to be aware of:
1. Weak Outdoor Signals
If the signal outside the metal building is already weak, the signal booster will have less to work with. In such cases, capturing a usable signal with the outdoor antenna becomes more challenging. This is particularly true in rural or remote areas where cell towers are few and far between.
To address this, consider using a high-gain directional antenna to capture the strongest possible signal from distant towers. This type of antenna focuses on a specific direction, allowing it to pull in weak signals from farther away.
2. Interference from Other Signals
In some industrial environments, metal buildings may house heavy machinery or equipment that generates electromagnetic interference, which can affect the performance of a signal booster. Careful placement of the indoor antenna away from such equipment can help mitigate this issue.
3. Dead Zones
Even with a signal booster, large metal buildings may still have areas where the signal does not reach, especially in corners or far from the indoor antenna. To eliminate dead zones, consider installing additional indoor antennas or using splitters to extend coverage to all areas of the building.
Overcoming Signal Challenges in Metal Buildings
Although metal structures are necessary for many businesses, maintaining dependable cell phone coverage can be challenging due to their signal-blocking qualities. By boosting poor external signals and rebroadcasting them inside the structure, signal boosters thankfully offer a practical answer. Cell reception in metal structures can be greatly enhanced by carefully positioning the external antenna, making sure that components are properly separated, and strategically situating the indoor antenna. Whether you live in a contemporary home with a metal roof, operate a business in a factory, or work in a sizable warehouse, a correctly installed signal booster can convert erratic, weak signals into strong, consistent connections, guaranteeing continuous communication and productivity.


