Staying connected in remote or difficult regions can be irritating when cellphone signals are weak or intermittent. Outdoor cellular antennas capture and amplify weak signals, making them a viable alternative for homes, businesses, and even rural properties. These antennas serve as the initial step in a signal booster system, resulting in better call quality, faster internet speeds, and a more dependable connection. In this detailed tutorial, we’ll look at how outdoor antennas work, the different types available, and how to choose the best one for your needs.
What is an Outdoor Cellular Antenna?
An outside cellular antenna, also known as a donor antenna, is meant to capture existing cellular signals in the air and send them to a signal booster for amplification. The amplified signal is then replayed indoors or throughout a certain area. Outdoor antennas often operate in the cellular frequency bands of 698-960 MHz and 1710-2700 MHz, ensuring compatibility with 4G LTE and 5G networks.
How Outdoor Cellular Antennas Work
Outdoor cellular antennas are a crucial part of a signal booster system. Here’s how they function:
- Signal Capture: The antenna collects weak cellular signals from the nearest tower.
- Signal Transmission: The captured signals are transmitted via cables to a signal booster.
- Amplification: The booster strengthens the signal and redistributes it to an indoor antenna or a target area.
The efficiency of this system depends heavily on the correct placement, alignment, and type of outdoor antenna used.
Types of Outdoor Cellular Antennas
Choosing the right outdoor antenna depends on your location, the strength of the signal, and your specific needs. Here are the most common types:
1. Omnidirectional Antennas
Omnidirectional antennas capture signals from all directions in a 360-degree pattern. They are straightforward to install and work well in areas with moderate to strong signals.
- Advantages:
- Easy installation and alignment.
- Can capture signals from multiple carriers and cell towers simultaneously.
- Effective in urban areas or locations with strong signal coverage.
- Disadvantages:
- Lower gain and range compared to directional antennas.
- Susceptible to interference and “signal noise.”

Omni Directional Antenna
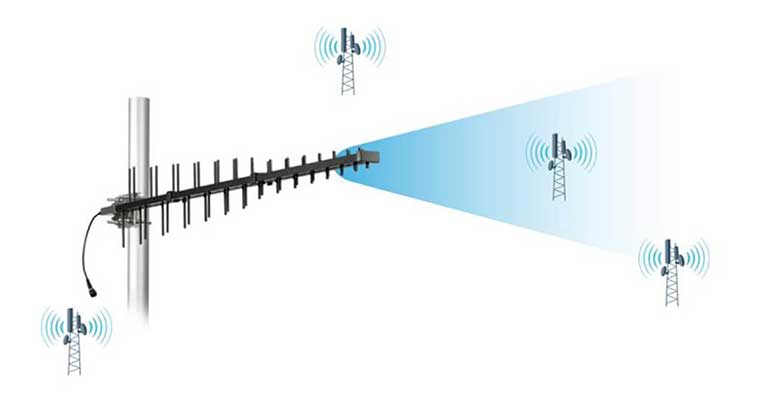
2. Yagi Antennas
Yagi antennas are unidirectional antennas that focus on a single direction to maximize signal reception. They are ideal for areas with weak signals and require precise alignment with the nearest cell tower.
- Advantages:
- Higher gain and longer range than omnidirectional antennas.
- Effective in rural or remote locations with distant cell towers.
- Disadvantages:
- Requires precise aiming for optimal performance.
- Limited to one carrier or tower at a time.
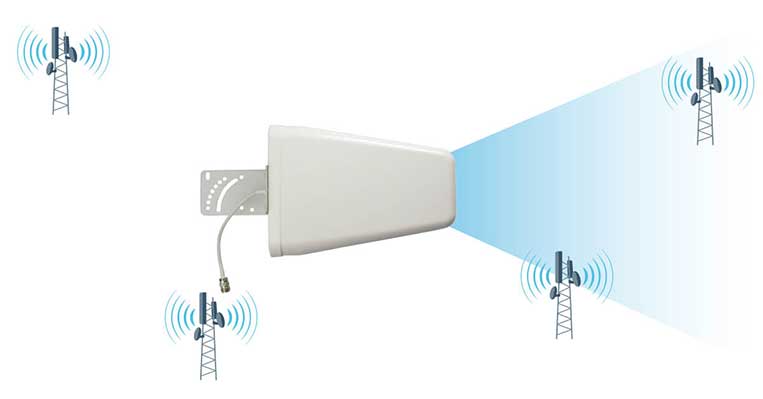
3. Log-Periodic Dipole Array (LPDA) Antennas
LPDA antennas are highly directional and known for their exceptional gain and wide frequency coverage. They are more advanced than Yagi antennas and are ideal for areas with very weak signals.
- Advantages:
- Highest gain among outdoor antennas.
- Capable of capturing signals over a broad frequency range.
- Effective in fringe or extremely remote areas.
- Disadvantages:
- More difficult to install and aim.
- Limited to a specific direction, requiring precise alignment.
Benefits of Using Outdoor Cellular Antennas
Investing in an outdoor cellular antenna offers a myriad of benefits, particularly for those in areas with limited cellular coverage. Key advantages include:
1. Improved Signal Strength and Quality
Outdoor antennas significantly boost the strength and clarity of cellular signals, reducing dropped calls, increasing data speeds, and enhancing overall mobile performance.
2. Expanded Coverage Area
By amplifying existing signals, outdoor antennas can extend the coverage area of a cell network, ensuring that even the most remote parts of a property receive reliable connectivity.
3. Enhanced Safety and Communication
Reliable cellular signals are crucial for emergency communications. Outdoor antennas ensure that you can make and receive calls during critical situations, providing peace of mind and improved safety.
4. Increased Productivity for Businesses
For rural businesses, such as farms, construction sites, or remote offices, consistent cellular connectivity is essential for operations, communication, and accessing online resources. Outdoor antennas facilitate seamless business activities by maintaining strong mobile signals.
5. Cost-Effective Solution
Compared to other connectivity solutions like satellite internet, outdoor cellular antennas offer a more affordable way to enhance mobile connectivity, making them an attractive option for both residential and commercial use.
Which Outdoor Antenna is Right for You?
Selecting the right outdoor antenna depends on your specific circumstances:
- For Urban or Suburban Areas: An omnidirectional antenna is ideal, especially if you need to capture signals from multiple carriers.
- For Rural Areas: A Yagi antenna offers excellent performance for moderately distant towers.
- For Remote or Fringe Areas: An LPDA antenna is the best choice for maximizing signal strength in the weakest signal zones.
Comparison Table: Omnidirectional vs. Yagi vs. LPDA Antennas
| Feature | Omnidirectional Antenna | Yagi Antenna | LPDA Antenna |
| Directionality | 360-degree coverage | Unidirectional | Highly directional |
| Gain | Low to moderate | Moderate to high | Highest |
| Range | Short to moderate | Moderate to long | Longest |
| Ease of Installation | Easy | Moderate | Challenging |
| Best Use Case | Urban areas with multiple towers | Rural areas with distant towers | Remote areas with very weak signals |
| Signal Capture | Captures all nearby signals (multi-carrier) | Focuses on one tower or carrier | Focuses on one tower with maximum gain |
Key Features to Consider When Choosing an Outdoor Cellular Antenna
Selecting the right outdoor antenna requires careful consideration of several factors to ensure optimal performance and compatibility with your specific needs. Key features to evaluate include:
1. Frequency Bands Supported
Ensure the antenna supports the frequency bands used by your cellular carrier. Common bands include 700 MHz, 800 MHz, 1700/2100 MHz, and 2600 MHz. Multi-band antennas offer greater flexibility and compatibility with various networks.
2. Gain (dBi)
Gain measures the antenna’s ability to amplify signals. Higher gain antennas provide stronger signal amplification but may require more precise aiming. Balance your need for signal strength with the feasibility of installation.
3. Type of Antenna
Decide between omnidirectional and directional antennas based on your location and the distribution of cell towers. Omni-directional antennas are ideal for areas with multiple towers, while directional antennas excel in single-tower environments.
4. Durability and Weather Resistance
Outdoor antennas must withstand various weather conditions, including rain, snow, wind, and extreme temperatures. Look for antennas with robust construction and weatherproof materials to ensure long-term performance.
5. Size and Mounting Options
Consider the size of the antenna and the available mounting locations. Ensure the antenna can be securely mounted in a location that provides optimal signal reception without causing obstructions or aesthetic concerns.
6. Compatibility with Existing Equipment
Verify that the outdoor antenna is compatible with your signal booster or amplifier system. Compatibility ensures seamless integration and optimal performance of your entire cellular enhancement setup.
7. Installation Requirements
Evaluate the complexity of the installation process. Some antennas require professional installation, especially directional models that need precise aiming, while others are designed for easier, DIY setups.
Top Outdoor Cellular Antenna Recommendations
Based on performance, reliability, and user reviews, here are some of the top outdoor cellular antennas available in the market:
1. Product Name
Overview:
Key Features:
Pros:
Cons:
Installation Tips for Outdoor Cellular Antennas
Proper installation is crucial to maximize the performance of your outdoor cellular antenna. Follow these best practices to ensure optimal signal reception and amplification:
1. Select the Ideal Mounting Location
Choose a location with a clear line of sight to the nearest cell tower. Rooftops, high poles, and open areas are ideal for mounting antennas to minimize obstructions that can weaken signal reception.
2. Use Quality Cabling
Invest in high-quality coaxial cables to connect the external antenna to the internal amplifier. Poor-quality cables can result in significant signal loss, reducing the effectiveness of the antenna.
3. Secure the Antenna Properly
Ensure the antenna is securely mounted to withstand harsh weather conditions, such as high winds and heavy rain. Use appropriate mounting hardware and techniques to prevent movement and damage.
4. Aim Directional Antennas Accurately
For directional antennas, precise aiming is essential. Use signal strength meters or smartphone apps designed to help locate and aim towards the cell tower for maximum signal capture.
5. Minimize Interference
Keep cables away from power lines and electronic devices that can cause interference. Use shielded cables and proper grounding techniques to reduce signal degradation.
6. Test and Optimize
After installation, test the signal strength in various locations within your coverage area. Make necessary adjustments to antenna placement and aim to achieve the best possible performance.
7. Consider Professional Installation
If you’re unsure about the installation process or require a complex setup, consider hiring a professional installer. Professional installation ensures optimal placement, alignment, and configuration of your outdoor antenna system.
Maintenance and Troubleshooting
Regular maintenance and prompt troubleshooting can extend the lifespan of your outdoor cellular antenna and ensure consistent performance.
1. Routine Inspections
Periodically inspect the antenna and cable for signs of wear, corrosion, or damage. Replace any damaged components to maintain signal integrity.
2. Clean the Antenna
Keep the antenna free from debris, bird nests, and other obstructions that can block signal reception. Gently clean the antenna surface to remove any buildup that may impede performance.
3. Check Connections
Ensure all connections between the antenna, cabling, and amplifier are secure and free from corrosion. Loose or corroded connections can significantly degrade signal quality.
4. Update Firmware
If your signal booster system includes smart features or firmware updates, ensure that your equipment is running the latest software to benefit from performance improvements and security enhancements.
5. Monitor Performance
Use signal monitoring tools to track the performance of your antenna system. Regular monitoring helps identify potential issues early, allowing for timely intervention and maintenance.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. Do I Need a Professional to Install an Outdoor Cellular Antenna?
While many outdoor antennas are designed for DIY installation, directional antennas may require professional installation to ensure precise aiming and optimal performance. If you’re uncomfortable with mounting equipment on rooftops or using tools, hiring a professional is recommended.
2. Can I Use an Outdoor Antenna with Any Signal Booster?
Most outdoor antennas are compatible with a wide range of signal boosters. However, it’s essential to verify compatibility with your specific booster model to ensure seamless integration and optimal performance.
3. How Much Does an Outdoor Cellular Antenna Cost?
Prices for outdoor cellular antennas vary based on type, gain, and features. Basic omnidirectional antennas can start around $100, while high-gain directional models can cost upwards of $500. Consider your specific needs and budget when selecting an antenna.
4. Will an Outdoor Antenna Work in All Weather Conditions?
High-quality outdoor antennas are designed to withstand various weather conditions, including rain, snow, and high winds. Ensure that the antenna you choose is rated for outdoor use and constructed with durable, weather-resistant materials.
5. How Do I Know Which Frequency Bands My Carrier Uses?
You can find information about your carrier’s frequency bands on their official website or by contacting customer support. Additionally, many online resources and coverage maps provide detailed information about the frequency bands used in your area.
The correct outside cellular antenna can improve cellular connectivity in remote regions. Understanding the many types of antennas, their capabilities, and the main elements to consider will allow you to select the ideal option for your needs. Whether you choose an omnidirectional antenna for broad coverage or a high-gain directional type for concentrated signal amplification, outdoor antennas are critical in closing the connectivity gap. Proper installation and frequent maintenance ensure that your antenna system provides dependable and robust cellular performance, allowing you to stay connected wherever you are. Invest in a high-quality outdoor cellular antenna today and enjoy the benefits of uninterrupted mobile connectivity beyond your home.


