In today’s fast-paced, technology-driven world, MIMO (Multiple Input, Multiple Output) antennas are at the heart of advanced wireless communications, powering everything from 5G networks to smart devices. However, not all MIMO antennas are created equal. Each type of MIMO antenna serves a specific purpose in optimising wireless communication. Understanding these antenna types and their applications allows for tailored solutions to meet diverse connectivity challenges, ensuring robust and reliable communication networks. Depending on your specific needs, choosing the right type of antenna can significantly impact your network’s performance. This guide explores various MIMO antenna types, including their advantages, use cases, and the latest advancements like MU-MIMO, SU-MIMO, and Massive MIMO.
Exploring MIMO Antenna Types
When selecting a MIMO antenna, the choice goes beyond the number of elements (e.g., 2×2 or 4×4). The design and functionality of the antenna itself play a crucial role in determining performance. Let’s examine the key types:
Dome (Ceiling) Antennas
Dome antennas are designed for indoor use, particularly within Distributed Antenna Systems (DAS), to provide consistent coverage in a specified area. Mounted on ceilings, these antennas radiate signals downward, ensuring even distribution of cellular or wireless signals across an indoor environment. They are commonly deployed in office buildings, malls, hospitals, and other large venues to improve indoor signal strength. With their seamless integration into ceiling tiles and omnidirectional coverage, dome antennas are a reliable choice for creating robust indoor networks.

Omni Antennas
Omnidirectional antennas, or omni antennas, radiate signals uniformly in all directions, offering 360-degree coverage. These antennas are most effective in environments with moderate signal strength and multiple cell towers nearby. Their primary advantage lies in their simplicity and versatility, making them ideal for WiFi systems, outdoor areas, and multi-carrier setups. However, due to their broad coverage, they provide lower gain compared to directional antennas, making them less suitable for remote areas or locations with weak signals.

Parabolic Dish Antennas
Parabolic dish antennas are highly directional, focusing signals into a concentrated beam for long-distance communication. Using a parabolic reflector, these antennas amplify signals from a specific direction, making them perfect for point-to-point links and backhauls in rural or remote locations. While they deliver exceptional range and gain, their effectiveness depends on precise alignment with the source signal, requiring careful installation and maintenance.

Panel Antennas
Panel antennas are flat, rectangular antennas designed for targeted coverage in a specific direction. Commonly used in outdoor wireless communication systems, they are a practical solution for mid-range applications where signals need to be concentrated within a defined area. Their compact design and reliability make them a popular choice for outdoor cellular signal enhancement, particularly for fixed installations.

Sector Antennas
Sector antennas are directional antennas that divide coverage into specific sectors, typically covering angles ranging from 60 to 120 degrees. These antennas are often found in cellular networks, where they serve as part of multi-sector configurations on base stations to ensure thorough area coverage. They are particularly useful in urban or semi-urban areas, providing strong, localised signals along roads or in densely populated regions.

Symmetrical Horn Antennas
Symmetrical horn antennas are characterised by their ability to deliver focused and symmetrical radiation patterns in both vertical and horizontal planes. Their design minimises interference and ensures consistent signal performance. These antennas are highly effective in point-to-point communication setups and high-frequency applications, offering precision and reliability in environments requiring directional coverage.

Smart Antennas
Smart antennas, also known as adaptive antennas, represent the forefront of MIMO technology. These antennas dynamically adjust their radiation patterns to optimise signal quality, reduce interference, and enhance capacity. They are essential in 5G networks, where they enable beamforming and other advanced features to manage high data demands in densely populated urban areas. Smart antennas are increasingly critical for modern wireless communication systems, ensuring seamless connectivity and efficient network performance.
Comparison Table: MIMO Antenna Types
| Antenna Type | Directionality | Gain | Best Use Case | Installation Complexity |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Dome (Ceiling) | Omnidirectional | Low | Indoor DAS systems for even coverage | Easy |
| Omni | Omnidirectional | Moderate | Multi-carrier setups in urban areas | Easy |
| Parabolic Dish | Highly Directional | High | Long-range communication links | High (requires precise aiming) |
| Panel | Directional | Moderate | Outdoor systems for focused coverage | Moderate |
| Sector | Semi-Directional | High | Cellular base stations | Moderate |
| Symmetrical Horn | Highly Directional | High | Point-to-point high-frequency setups | Moderate |
| Smart Antennas | Adaptive Directional | High | 5G networks and dense urban environments | High |
Choosing the Right MIMO Antenna
Your choice of antenna depends on specific needs.
- Coverage Requirements: For large frequency ranges, choose log-periodic or omni antennas. For focused, directional coverage, opt for panel or dish antennas.
- Range: Dish antennas deliver the best long-range performance, while log-periodic or panel antennas work well for shorter ranges.
- Environment: Omni antennas are great for mobile or multi-carrier scenarios, while directional antennas (e.g., panel or dish) are better for stationary setups.
Advanced MIMO Variants: MU-MIMO, SU-MIMO, and Massive MIMO
MIMO technology has evolved to meet diverse user and network requirements. Here’s a breakdown of the main variants:
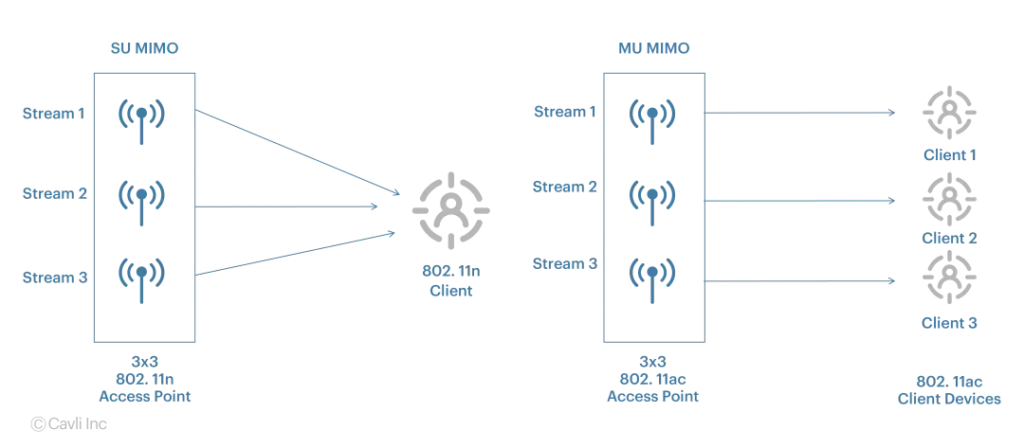
1. MU-MIMO (Multi-User MIMO)
MU-MIMO enables a single MIMO antenna to communicate with multiple devices simultaneously. By splitting bandwidth into separate streams, this technology
- Enhances network efficiency in crowded environments.
- Is perfect for homes and offices with numerous connected devices.
- It requires both the antenna and the connected devices to support MU-MIMO for optimal performance.
2. SU-MIMO (Single-User MIMO)
SU-MIMO, the traditional MIMO setup, focuses on boosting performance for a single device. Features include:
- Spatial Multiplexing: Sends unique data streams through each antenna for increased speed.
- Diversity Coding: Uses multiple antennas to improve signal reliability.
SU-MIMO is widely used in consumer Wi-Fi and cellular systems, offering a solid balance of speed and dependability.
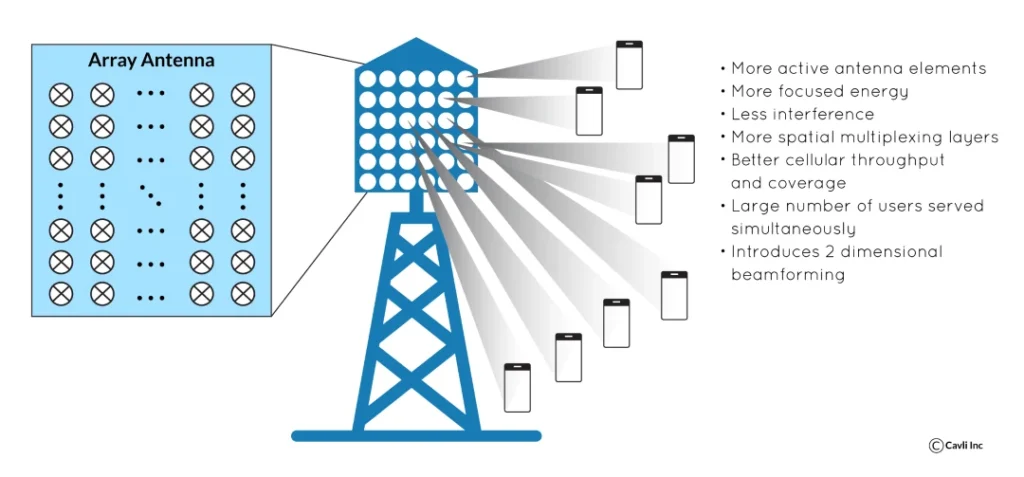
3. Massive MIMO
Massive MIMO takes the concept to the next level by deploying hundreds of antennas in large-scale systems like 5G networks. Its advantages include:
- Advanced beamforming, focusing signals toward individual users.
- Drastically improved capacity and data rates for large-scale systems.
Massive MIMO is essential for high-demand scenarios like smart cities, industrial IoT, and autonomous vehicle networks.
Elevating Connectivity with the Right MIMO Antenna
Selecting the right MIMO antenna can significantly enhance your wireless communication experience, whether for home, office, or industrial applications. From understanding different antenna types to leveraging advanced technologies like MU-MIMO and Massive MIMO, the key lies in matching the solution to your unique requirements. By doing so, you can unlock faster speeds, stronger signals, and more reliable connectivity—paving the way for seamless digital experiences in a connected world.


